Led Torch
LEDs are becoming increasingly popular in many lighting applications. White LEDs are now common in torches.
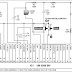
Here’s a simple and economical LED torch that operates off two 1.5V cells. For a white LED, the forward conduction voltage and the forward current are 3.6V and 20 mA, respectively. Capacitor C1, the transistor, and the transformer form a self-oscillating DC-DC converter. The transformer boosts the input battery voltage and supplies a high voltage to the white LEDs. Diode D1 and smoothing capacitor C2 supply the high voltage to the LED chain via resistor R2.
Here’s a simple and economical LED torch that operates off two 1.5V cells. For a white LED, the forward conduction voltage and the forward current are 3.6V and 20 mA, respectively. Capacitor C1, the transistor, and the transformer form a self-oscillating DC-DC converter. The transformer boosts the input battery voltage and supplies a high voltage to the white LEDs. Diode D1 and smoothing capacitor C2 supply the high voltage to the LED chain via resistor R2.
The light intensity is affected by the input battery voltage. As the transformer is not readily available in the market, you may need to build it yourself. The transformer windings also affect the light intensity. The transformer coil is wound on a 4mm thick ferrite toroid having 13mm outer diameter and 6mm inner diameter.
Primary windings comprise 4 turns and secondary windings 55 turns of 36SWG copper-enamelled wire on toroid transformer core as shown on the right side in the figure. For the long life of 1.5V cells, keep switch S1 in ‘on’ position only when the torch is in use.
Primary windings comprise 4 turns and secondary windings 55 turns of 36SWG copper-enamelled wire on toroid transformer core as shown on the right side in the figure. For the long life of 1.5V cells, keep switch S1 in ‘on’ position only when the torch is in use.









No comments:
Post a Comment